CNS Drug Disposition
Transpharmation is committed to improving the success of new drugs by offering translational models and transformative research services. For CNS targeted therapeutics, the disposition of a drug in the brain is a vital factor in understanding its efficacy and safety profile. With a combination of state-of-the-art techniques and extensive CNS development expertise, Transpharmation is able to provide support for critical lead selection and development decisions, thereby helping improve the quality of clinical candidates.
Models
-
- Simultaneous collection of brain tissue and plasma from the same animal followed by LC-MS/MS bioanalysis of compound concentrations
- Brain and plasma free-fraction determination using equilibrium dialysis
- Useful for early-stage screening and lead selection programs, and can be combined with efficacy or POC studies
-
- Industry accepted gold-standard model for determining unbound drug concentrations in specific brain regions over time
- Combined drug and biomarker assessment enables PK-PD studies to establish robust dose-response profiles
- In vitro and in vivo parameters are optimized for each compound to ensure accuracy and reliability of results which can be used to support development decisions.
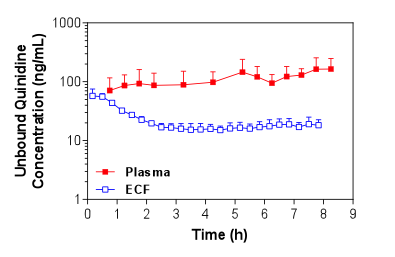 Figure 1. Mean + S.D. (n=4) unbound plasma and brain ECF concentrations of quinidine in Sprague-Dawley rats over time following i.v. administration of a loading dose and constant rate infusion of quinidine.
Figure 1. Mean + S.D. (n=4) unbound plasma and brain ECF concentrations of quinidine in Sprague-Dawley rats over time following i.v. administration of a loading dose and constant rate infusion of quinidine.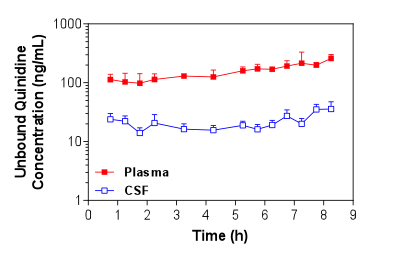 Figure 2. Mean + S.D. (n=5) unbound plasma and CSF concentrations of quinidine in Sprague-Dawley rats over time following i.v. administration of a loading dose and constant rate infusion of quinidine.
Figure 2. Mean + S.D. (n=5) unbound plasma and CSF concentrations of quinidine in Sprague-Dawley rats over time following i.v. administration of a loading dose and constant rate infusion of quinidine. -
- ~150 beagle dogs of various ages are available for CSF and plasma sampling studies to evaluate drug delivery and exposure in a clinically relevant non-rodent species
- Efficacy and safety profiles of new drugs can be further characterized by assessing drug or biomarker levels in CSF and plasma from the same animal over time
- Aged dogs provide a natural and translational model for various age related conditions such as Alzheimer’s Disease progression, Osteoarthritis and Cancer
-
- Collecting serial samples of CSF and plasma via surgically implanted catheters allows the determination of unbound drug delivery into the brain in awake rats
- Reduced inter-animal variability improves quality and power of data over parallel sampling techniques
- Studies can be performed in SAGE® ADME knockout rats to investigate how specific drug transporters affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs
- Data rich study designs have demonstrated predictive validity in characterizing drug delivery into the brain 1
- Fan, J. et. al. Drug Metabolism Reviews.44(S1):138-139 (2012)
-
- Non-survival sampling of cerebrospinal fluid from the cisterna magna of mice can be used to estimate free drug concentrations in the brain following drug administration
- Can be combined with brain tissue harvesting and plasma collection to understand differences in drug exposure for CSF, brain and plasma
- Also useful as an addition to efficacy or POC studies